How to set and use environment variables in Node.js service
Environment variables help you run your application in different environments. They allow you to isolate all specific environment aspects from your application code and keep your app encapsulated.
In Zerops you do not have to create a .env file manually. Zerops handles the environment variables for you.
Service env variables
Zerops supports service-level environment variables that are specific to your Node.js service. There are 3 different sets of service env variables in Zerops:
| Type | Environment | Defined in |
|---|---|---|
| basic | build | zerops.yaml |
| basic | runtime | zerops.yaml |
| secret | runtime | Zerops GUI |
Zerops also supports project-level environment variables that apply across all services within a project.
Use the secret env variables for all sensitive data you don't want to store in your application code. Secret env variables are also useful if you need for testing where you need to change the value of some env variables frequently. Secret variables are managed in Zerops GUI and you don't have to redeploy your application.
The basic build and runtime env variables are listed in your zerops.yaml and deployed together with your application code. When you need to update a value of an existing env variable or change the set of build or runtime env variables, update your zerops.yaml and redeploy your application to Zerops.
You can reference another variable of the same service or even a variable of another service within the same project.
Set secret env variables in Zerops GUI
Use secret variables to store passwords, tokens and other sensitive information that shouldn't be part of your repository and listed in zerops.yaml.
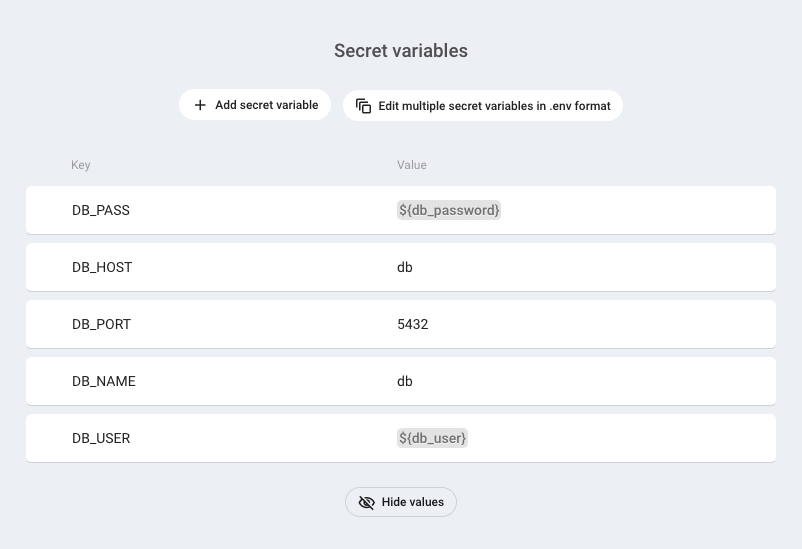
You can set env variables when you create a new Node.js service or you can set them later.
To configure env variables for an existing service, go to the service detail and choose Environment variables in the left menu. Scroll to the Secret variables section and click on the Add secret variable button and set variable key and value.
You can edit or delete env variables that you've created by clicking on the menu on the right side of each row.
The changes you've made to environment variables will be automatically applied to all containers of your project's services.
You need to restart the runtime service after you update environment variables. The Node.js process running in the container receives the list env variables only when it starts. Update of the env variables while the Node.js process is running does not affect your application.
Set basic build env variables in zerops.yaml
To set basic env variables for the build environment, add the envVariables attribute to the build section in your zerops.yaml
When you need to update a value of an existing env variable or change the set of build or runtime env variables, update your zerops.yaml and redeploy your application to Zerops.
Set basic runtime env variables in zerops.yaml
To set basic env variables for the runtime environment, add the envVariables attribute to the runtime section in your zerops.yaml.
When you need to update a value of an existing env variable or change the set of build or runtime env variables, update your zerops.yaml and redeploy your application to Zerops.
Env variable restrictions
key
- must satisfy the following regular expression:
[a-zA-Z_]+[a-zA-Z0-9_]* - all variable keys in the same service must be unique regardless of case
- keys are case sensitive
value
- must contain only ASCII characters
- the End of Line character is forbidden
These restrictions apply to all types of env variables.
Referencing other env variables
You can reference another variable of the same service using ${key} in your variable value. You can even reference a variable from a different service using ${hostname_key}. The referenced variable doesn't need to exist when you are entering your variable.
Reference a local variable in another variable value
| Variable key | Variable value | Computed variable value |
|---|---|---|
| id | 12345 | 12345 |
| hostname | app | app |
| name | ${id}-${hostname} | 12345-app |
Reference a variable of another project service
Let's say your project contains two PostgreSQL services dbtest and dbprod. Both services have a connectionString variable. Then you can create a dbConnectionString env variable in your Node.js runtime and set ${dbtest_connectionString} as the variable value. Zerops will fill in the value of the connectionString variable of the dbtest service.
When you change the dbConnectionString value to ${dbprod_connectionString}, Zerops will fill in the value of the connectionString variable of the dbprod service.
When you change the value of the connectionString variable in the service dbtest you need to restart the Node.js service. The Node.js process running in the container receives the list env variables only when it starts. Update of the env variables while the Node.js process is running does not affect your application.
Generated env variables
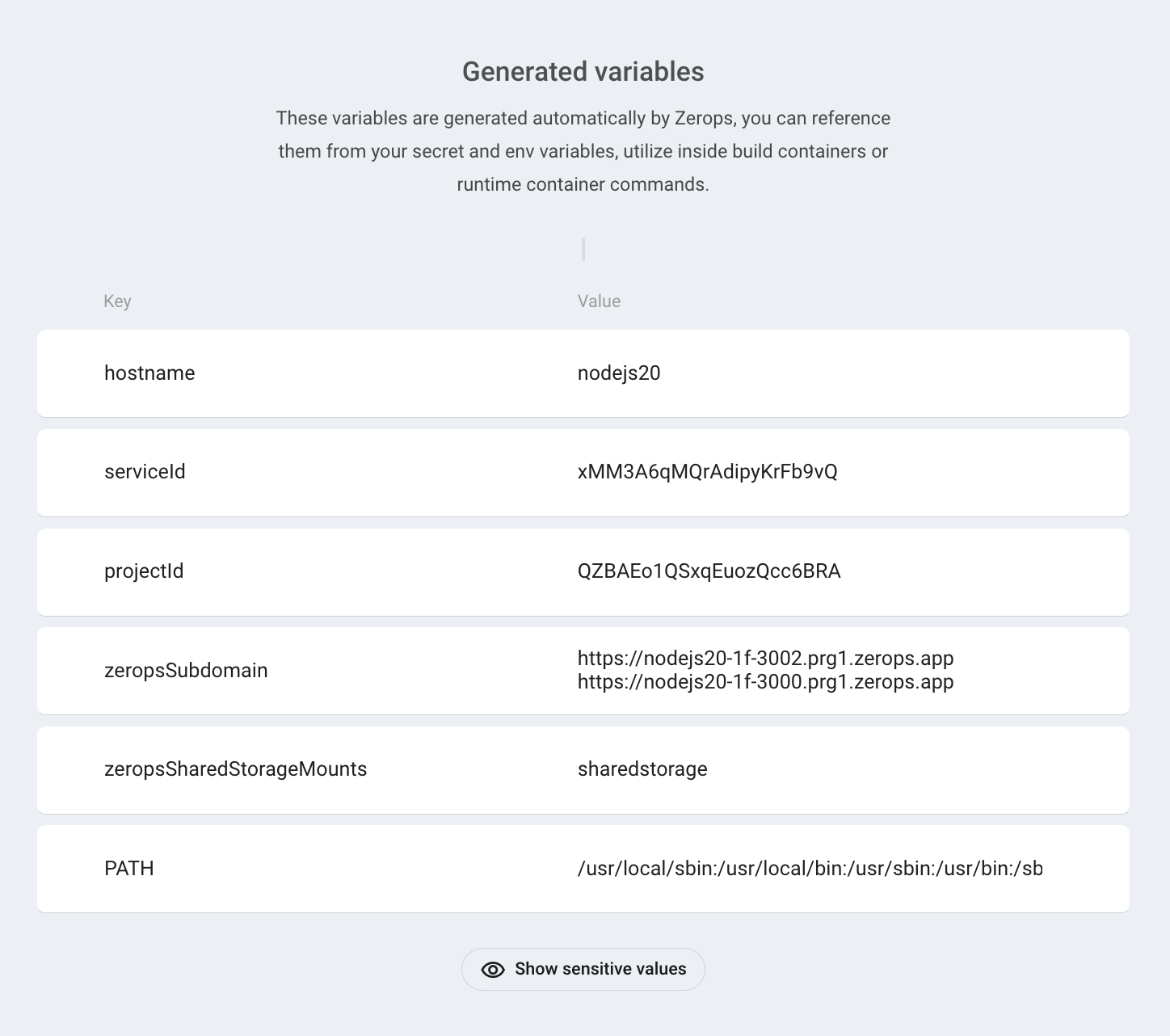
Zerops creates several helper variables when a Node.js service is created, e.g. hostname, PATH. Some helper variables are read-only (hostname), others are editable (PATH). Generated variables cannot be deleted.
Generated env variables are listed on the Environment variables page. Scroll to the Generated variables section.
How to read env variables from your Node.js app
Zerops passes all environment variables from all project services when your Node.js app is deployed and started.
To access the local environment variable i.e. the variable set to this Node.js service in your app, use:
How to read env variables of another service
All services of the same project can reference environment variables from other services. To use an environment variable from one service in another service in the same project, you must prefix the environment variable key with the service hostname and underscore.
Examples:
To access the connectionString env variable of the mariadb1 service, use mariadb1_connectionString as the env variable key.
To access the password env variable of the mariadb2 service, use mariadb2_password as the env variable key.
How to read runtime env variables in the build environment
You can use runtime env variables in the build environment using the RUNTIME_ prefix. For example if you have a runtime variable with the connectionString key, use the RUNTIME_connectionString to read the variable in the build environment. This rule applies both for basic and secret runtime variables.
Basic and secret env variable with the same key
If you create a secret env variable and a basic runtime env variable with the same key, Zerops saves the basic runtime env variable from your zerops.yaml and ignores the secret env variable.
If you create a basic build env variable and a runtime env variable with the same key, Zerops saves both because the build and runtime environments have separate sets of env variables.