Environment Variables
Zerops manages environment variables at two scopes: service level and project level. These variables are handled automatically without requiring .env files.
On this page: Service Variables · Project Variables · Referencing Variables · Variable Isolation · Restrictions · Examples
Service Variables
Variables that are specific to individual services.
User-Defined Variables
You can define service-level variables in two ways:
1. Build & Runtime Variables
These variables are defined with envVariables attribute in the build or run section of your zerops.yaml file and are accessible within their respective containers.
See how to reference variables between services and between build and runtime environments. All variables must follow the naming restrictions.
Your application must be redeployed when updating environmental variables in zerops.yaml.
2. Secret Variables
For storing sensitive data you don't want in your source repository. They can be updated without redeployment (though services need to be reloaded).
Secret variables can be managed through:
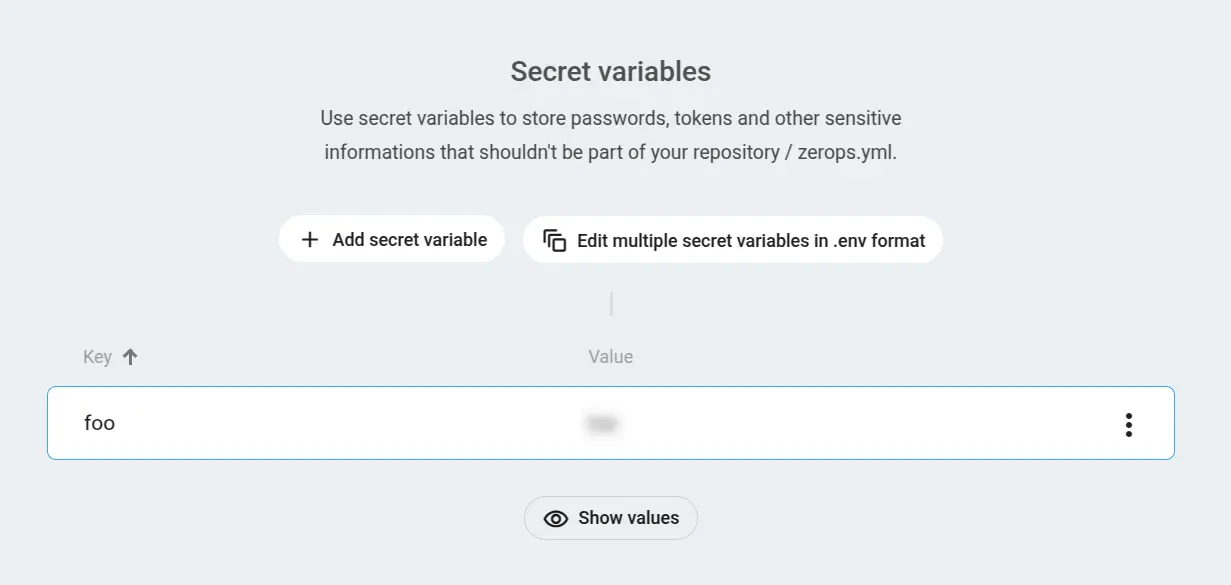
GUI Interface
Navigate to service details and find Environment variables in the menu. You can:
- Add individual variables using the "Add secret variable" button
- Edit individual variables through the menu that appears on hover
- Use the bulk editor for managing multiple variables in .env format
Import Configuration
Create secret variables for a service with envSecrets attribute. See the complete import.yaml structure.
System-Generated Variables
Zerops automatically generates variables based on service type.
These variables cannot be deleted and are always listed at the bottom of the environment variables page. Some are read-only (like hostname), while others can be edited (like PATH).
These variables can also be referenced.
Project Variables
Variables that apply across all services within a project. These provide a way to share common configuration across services.
They work similarly to service secret variables but at project scope - they're managed through the GUI and can be updated without redeployment (though services need to be reloaded).
Project variables are automatically inherited by all services in the project — both in build and runtime environments. You do not need to reference them in your zerops.yaml.
User-Defined Variables
You can set project-wide variables through:
GUI Interface
Access Project environment variables in your project detail to:
- Add individual variables one by one
- Edit individual variables
- Use the bulk editor with .env format
Import Configuration
Create project variables with envVariables attribute. See the complete import.yaml structure.
These variables will be automatically available in all services without any additional configuration.
System-Generated Variables
Zerops automatically generates project-level variables that are also automatically available in all services.
Overriding Project Variables
If you need a different value for a specific service, you can override a project variable by defining a service-level variable with the same key. See Variable Precedence for details on how conflicts are resolved.
Environment Variable Isolation
A security feature that controls the visibility of environment variables across services within a project. This affects how referencing variables across services works.
By default, Zerops isolates environment variables between services to enhance security and prevent unintended access to sensitive information. This isolation can be configured at both project and service levels.
Isolation Modes
Zerops supports two isolation modes:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
service | Default mode. Variables are isolated to their respective services. Services can only access their own variables and must explicitly reference variables from other services. |
none | Legacy mode. All variables from all services are automatically shared and accessible via prefixing. |
Configuring Isolation
Project-Level Isolation
Zerops automatically creates the envIsolation project variable with the default value service. You only need to modify this if you want to disable isolation:
This can also be set through the Project Environment Variables section in the GUI.
Service-Level Override
Individual services can override the project-level isolation setting:
You might set a database service to envIsolation: none to expose its connection details to other services, without having to manually reference them, while keeping the rest of your services isolated.
In import YAML, envIsolation can also be nested under envVariables/envSecrets. (If both are present, the nested version takes precedence).
Accessing Variables Across Services
With Isolation Enabled (service mode)
When isolation is enabled, you must explicitly create reference variables to access variables from other services:
This approach gives you complete control over which variables are shared between services.
With Isolation Disabled (none mode)
When isolation is disabled, variables are automatically available across all services with the service name prefix:
Best Practices for Variable Isolation
- Use Default Isolation: Keep the default
serviceisolation for enhanced security. - Explicit References: Create explicit references only for variables that need to be shared.
- Naming Conventions: Use clear naming patterns for reference variables (e.g.
DB_PASSWORDfor a reference todb_password). - Service-Level Exceptions: Use service-level isolation overrides sparingly and only for services that need to expose their variables widely.
Referencing Variables
You can reference other variables using the ${variable_name} syntax. This is used to reference service-level variables, not project variables (which are already automatically inherited).
Within Same Service
Across Services
How this works depends on your environment variable isolation setting:
With Isolation Enabled (service mode - default)
Create an explicit reference in the destination service:
With Isolation Disabled (none mode)
Variables from other services are automatically injected into the container and available using the service prefix format servicename_variablename:
Between Build and Runtime Environments
Build and runtime are two distinct environments in Zerops. Each environment can have its own set of variables, and you can use the same variable names in both environments since they are separate. Due to this separation, variables defined in one are not automatically accessible in the other.
To share variables between environments, you need to use specific prefixes:
- Use
RUNTIME_prefix to access runtime variables during build - Use
BUILD_prefix to access build variables during runtime
Project Variables — No Reference Needed
Project variables are automatically available in all services. Do not use the ${...} syntax to reference them:
If a project variable is named LOG_LEVEL, your application can read it directly — you don't need to add anything to your zerops.yaml.
Variable Restrictions
All environment variables must follow these restrictions:
Key
- Alphanumeric characters only (use
_to separate words) - Must be unique within their scope
- Case-sensitive
Value
- ASCII characters only
- No EOL characters
Variable Management
Variable Precedence
When the same environment variable key exists in multiple places, Zerops follows these precedence rules:
- Service-level variables take precedence over project variables
- Within service-level:
- Build/runtime variables override secret variables
- Build and runtime containers are separate environments
Environment Variable Examples
Variable Isolation Example
Consider a project with three services: api, db, and cache:
project:
name: my-project
services:
- hostname: api
envSecrets:
# Creating explicit references to needed variables
DB_CONNECTION: ${db_user}:${db_password}@${db_hostname}:${db_port}
CACHE_URL: ${cache_hostname}:${cache_port}
- hostname: db
envSecrets:
password: secureDbPassword
user: dbuser
port: 5432
- hostname: cache
envSecrets:
password: cacheServerPass
port: 6379
With this setup:
- The
apiservice can only access the specificdbandcachevariables it explicitly references - The
dbservice cannot see any variables fromapiorcache - The
cacheservice cannot see any variables fromapiordb
If we changed the project's envIsolation to none, all services would be able to see all variables from all other services (prefixed with the service name).
Need help? Join our Discord community.